🩺 Understanding Leukemia: A Complete Patient Guide
Meta Description (SEO): Learn about leukemia, its types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and coping strategies. Comprehensive guide for patients worldwide.
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer affecting bone marrow and lymphatic tissue, leading to abnormal production of white blood cells. This guide covers all aspects of leukemia, helping patients understand, manage, and cope with the disease.
🔬 What is Leukemia?
Leukemia is a progressive, malignant disease of the blood-forming tissues. It primarily starts in the bone marrow and can affect other organs. It is characterized by the uncontrolled production of immature or abnormal white blood cells, which interferes with normal blood cell production.
- Acute leukemia: Rapid onset and fast progression; immature white blood cells (blasts) proliferate quickly.
- Chronic leukemia: Slow-developing; abnormal cells may resemble mature blood cells and progress over years.
Types of Leukemia
Leukemia is generally classified into four main types:
| Type | Description | Commonly Affected Age | Speed of Progression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) | Immature lymphoid cells (lymphoblasts) | Mostly children | Rapid |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | Immature myeloid cells (myeloblasts) | Adults | Rapid |
| Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Mature-appearing lymphocytes | Adults >60 | Slow |
| Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) | Mature myeloid cells | Adults | Slow |
💡 Did You Know? Acute leukemias require immediate treatment, whereas chronic forms may remain undetected for years.
🧬 How Leukemia Develops
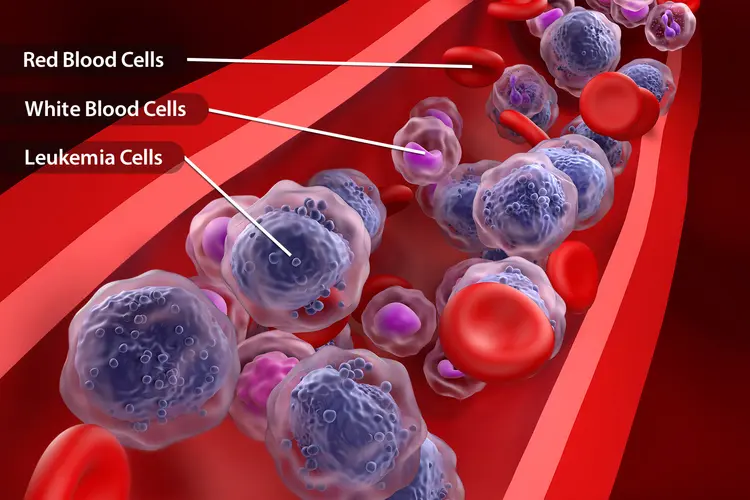
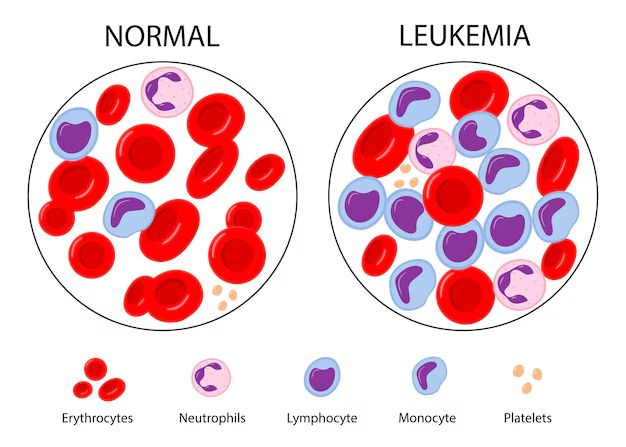
Leukemia begins when a bone marrow cell undergoes abnormal changes. These leukemia cells grow uncontrollably, live longer than normal cells, and gradually replace healthy blood cells.
Bone marrow produces:
- Red blood cells: Carry oxygen to tissues.
- White blood cells: Fight infections.
- Platelets: Help blood clotting.
In leukemia:
- Acute leukemias (ALL & AML): Blast cells multiply rapidly, crowding out normal cells → anemia, infection, bleeding.
- Chronic leukemias (CML & CLL): Some normal function persists, but high white blood cell counts can cause complications over time.
⚠️ Who is at Risk?
Leukemia can affect any age, but adults over 60 are more commonly affected. Children mostly develop ALL.
Risk factors may include:
- Previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy
- Genetic disorders (e.g., Down syndrome)
- Chemical exposures (benzene)
- Smoking and lifestyle factors
🔬 Leukemia is not contagious.
🩺 Symptoms and Clinical Signs
Leukemia symptoms vary by type:
| Symptom | Acute Leukemia (AML/ALL) | Chronic Leukemia (CML/CLL) |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue & weakness | ✅ | ✅ (may appear later) |
| Shortness of breath | ✅ | ✅ |
| Pale skin | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fever & night sweats | ✅ | Sometimes |
| Easy bruising / bleeding | ✅ | Sometimes |
| Swollen lymph nodes | Sometimes | ✅ |
| Bone & joint pain | ✅ | Sometimes |
| Frequent infections | ✅ | ✅ |
| Weight loss | ✅ | ✅ |
💡 Doctor’s Tip: Persistent fatigue, unexplained bruises, or recurring infections should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Children may show additional signs:
- Rapid weight loss
- Abdominal swelling
- Persistent fever
- Bone/joint pain
🔬 Diagnosis of Leukemia
Leukemia diagnosis typically involves:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Checks red cells, white cells, and platelets.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Confirms leukemia and identifies subtype.
- Imaging (X-ray, CT): Evaluates organ involvement.
- Molecular and cytogenetic tests: Detect genetic abnormalities affecting treatment decisions.
Table: Diagnostic Tests and Purpose
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CBC | Detect abnormal blood counts |
| Bone marrow aspiration / biopsy | Confirm leukemia type |
| CT scan | Check organ involvement |
| Lumbar puncture | Detect leukemia in cerebrospinal fluid |
| Cytogenetic / molecular tests | Identify genetic mutations for treatment |
💊 Treatment Options
Leukemia treatment depends on type, age, overall health, and genetic subtype. Goals: complete remission and quality of life.
Acute leukemia (ALL & AML):
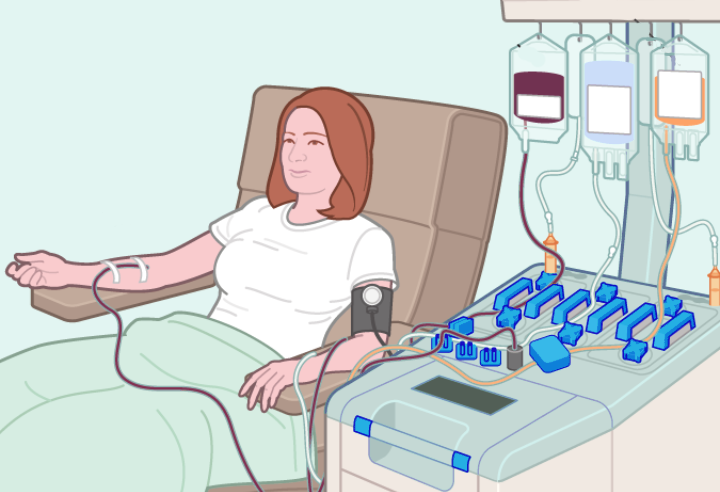
- Chemotherapy: Induction, consolidation, maintenance
- Bone marrow / stem cell transplant: For high-risk or relapsed patients
Chronic leukemia (CML & CLL):
- Targeted therapy (e.g., Imatinib, Dasatinib for CML)
- Chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies (for CLL)
- Allogeneic stem cell transplant: Selected patients
Table: Common Treatments by Type
| Leukemia Type | First-Line Treatment | Optional / Advanced Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | Chemotherapy | Stem cell transplant |
| AML | Chemotherapy | Stem cell transplant |
| CLL | Watchful waiting / Chemotherapy | Monoclonal antibodies, Transplant |
| CML | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | Allogeneic stem cell transplant |
💡 Did You Know? More than 5-year remission is increasingly common in leukemia patients with modern therapies.
📈 Survival Rates & Prognosis
| Leukemia Type | Approx. 5-Year Survival | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ALL (children) | 85% | Excellent response to modern chemo |
| ALL (adults) | 40–50% | Varies by age and genetics |
| AML | 30–40% | Depends on subtype and risk factors |
| CLL | 80–90% | Slow progression |
| CML | 70–90% | With targeted therapy |
💡 Prognosis is highly individual. Early diagnosis and specialized treatment improve outcomes.
❤️ Social & Emotional Impact
Leukemia diagnosis can be emotionally overwhelming. Patients benefit from:
- Learning about their type and treatment options
- Seeking emotional support from healthcare teams, family, or patient groups
- Understanding long-term effects such as fatigue, cognitive changes, and infection risk
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Leukemia
🩺 Q1: What are the early signs of leukemia?
A: Early leukemia symptoms can be subtle and resemble common illnesses. Look for:
- Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Pale skin due to anemia
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding (nosebleeds, gum bleeding)
- Frequent infections or slow healing of wounds
- Night sweats and low-grade fevers
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Sudden weight loss or loss of appetite
💡 Tip: If these symptoms persist for more than 2 weeks, see a hematologist immediately.
💉 Q2: How is leukemia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis usually involves several steps:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures red cells, white cells, and platelets.
- Peripheral blood smear: Checks for abnormal cells in blood.
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: Confirms leukemia type and stage.
- Cytogenetic and molecular tests: Detect gene mutations and chromosomal abnormalities that affect treatment.
- Imaging tests (CT/MRI): Check for organ involvement or swollen lymph nodes.
🧬 Tip: Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
💊 Q3: What treatments are available for leukemia?
A: Treatment depends on leukemia type, age, overall health, and genetic subtype:
| Leukemia Type | Standard Treatment | Advanced Options |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | Chemotherapy | Stem cell transplant, targeted therapy |
| AML | Chemotherapy | Stem cell transplant, clinical trials |
| CLL | Observation / Chemotherapy | Monoclonal antibodies, targeted therapy, transplant |
| CML | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (Imatinib, Dasatinib) | Stem cell transplant if resistant |
💡 Tip: Treatment plans are personalized. Always consult a specialized hematologist.
🩺 Q4: Can leukemia be cured?
A: Many leukemias can be controlled or cured:
- Acute leukemia (ALL/AML): Early treatment can lead to complete remission.
- Chronic leukemia (CLL/CML): May be managed effectively for many years with targeted therapy; some cases may achieve long-term remission.
💡 Tip: Ongoing monitoring is essential even after remission.
🧬 Q5: What lifestyle changes help manage leukemia?
A: While lifestyle cannot cure leukemia, these measures support treatment and overall health:
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet 🍎
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
- Maintain moderate physical activity as tolerated 🏃♂️
- Prevent infections (hand hygiene, vaccinations, avoiding sick contacts)
- Monitor blood counts regularly
💉 Q6: Are leukemia treatments painful or risky?
A: Treatments like chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant can have side effects:
- Fatigue, nausea, hair loss, low immunity
- Pain at injection or biopsy sites
- Risk of infection due to low white blood cells
💡 Tip: Supportive care, medications, and hospital monitoring minimize complications.
❤️ Q7: How does leukemia affect daily life and emotions?
A: A leukemia diagnosis can impact:
- Physical energy (fatigue, weakness)
- Emotional wellbeing (stress, anxiety, depression)
- Social life (hospital visits, isolation to prevent infection)
Support strategies:
- Join patient support groups
- Discuss mental health with professionals
- Plan daily activities around energy levels
🧬 Q8: What is the role of stem cell or bone marrow transplant?
A: Transplants replace diseased bone marrow with healthy cells:
- Often used for high-risk or relapsed leukemia
- Can achieve long-term remission or cure
- Requires compatible donor and careful monitoring
💡 Tip: Not all patients are candidates; doctors evaluate age, health, and leukemia subtype.
💊 Q9: Can leukemia recur after treatment?
A: Yes, relapse is possible:
- Acute leukemias may relapse within months if high-risk factors exist
- Chronic leukemias can progress slowly even after long-term control
Tip: Regular follow-up, blood tests, and bone marrow evaluations help detect relapse early.